The Role of Laminating in Flexible Packaging
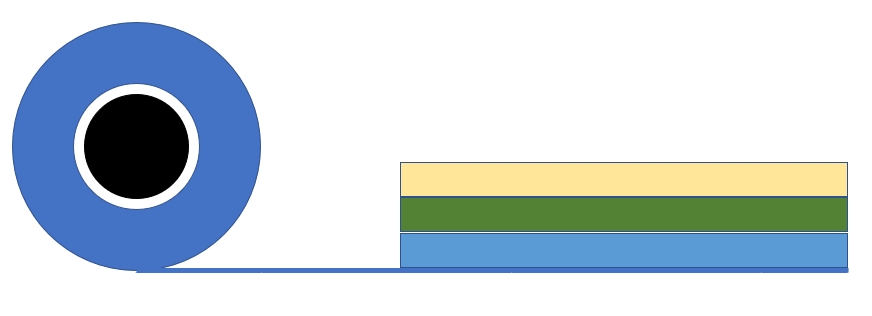
Q: What type of application requires lamination?
The purpose of the laminating process is to produce a final flexible packaging with enhanced barrier properties, appearance and strength. Therefore, it can be applied to any applications that are looking for enhanced barrier properties, appearance and strength. Typically, lamination is found in an application where the product needs the packaging to extend its shelf life and to keep it fresh. A common application is the food industry. In the food industry laminated flexible packaging is applied to read-to-eat products such as ice creams, potato chips, snacks and drinks. At the same time applied to uncooked food such as boil-in a-bag pouches, freezer-to-microwave products, vegetables and meat. Besides the food industry, lamination is also found in other industries such as electronics, garment, cosmetics, and medical.
Q: When is the lamination performed during the flexible packaging production?
Lamination usually takes place after printing and before slitting.
Q: What are the trends for lamination?
The general trend for lamination is towards a more environmentally friendly process. To achieve this, companies are trying to reduce the number of lamination layers. At the same time to replace less recyclable materials with more recyclable materials and bio-degradable bonding agents. For instance, traditionally aluminum foil is a commonly used lamination layer as it provides superb strength and barrier properties for the packaging. A common application of the aluminum foil is to laminate it against PET on one side and PE on the other to form a 3-layer final product. Now companies are trying to get rid of the aluminum foil with a layer of coated adhesive such as AIOx or SiOx to form a 2-layer final product.

Article by Daywey Chen, KYMC